Neuroprotection and Neuroenhancement in Ophthalmology
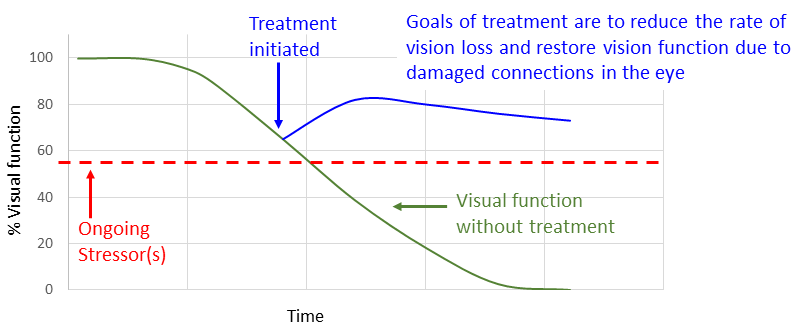
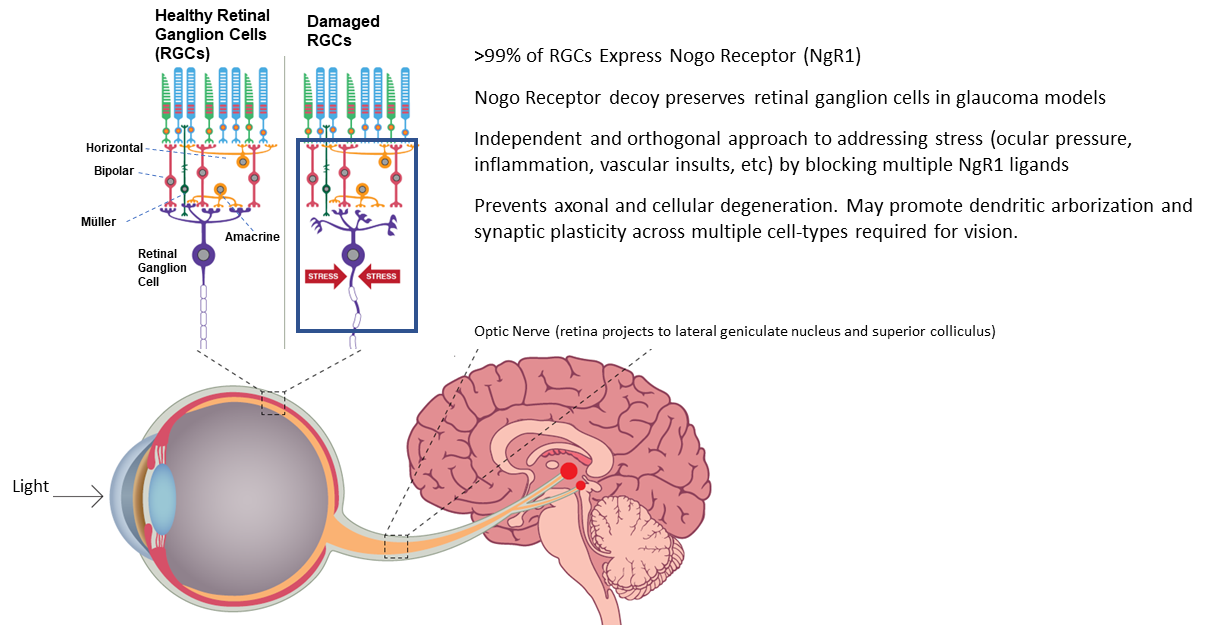
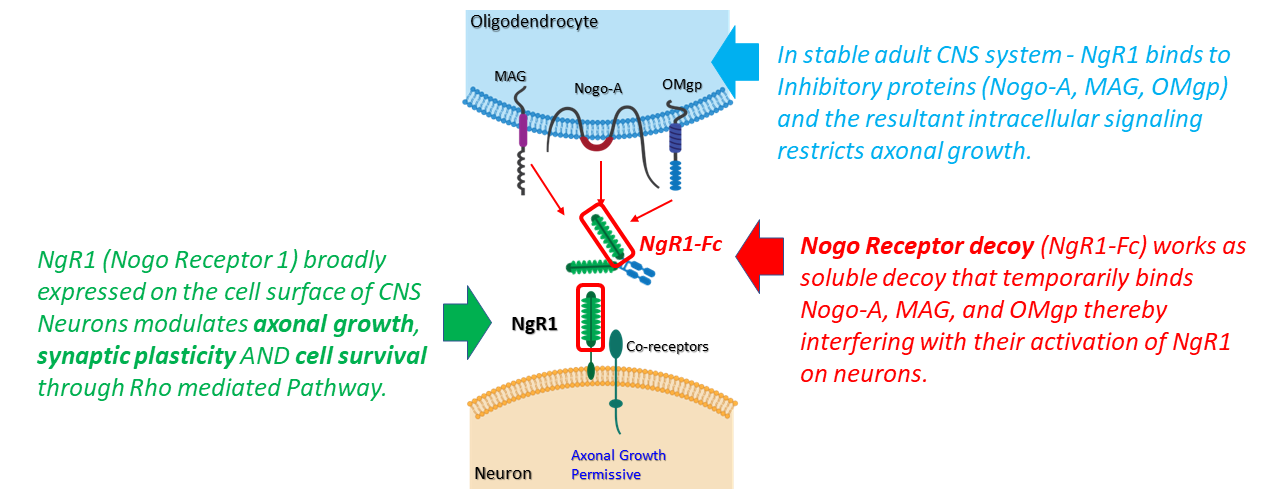
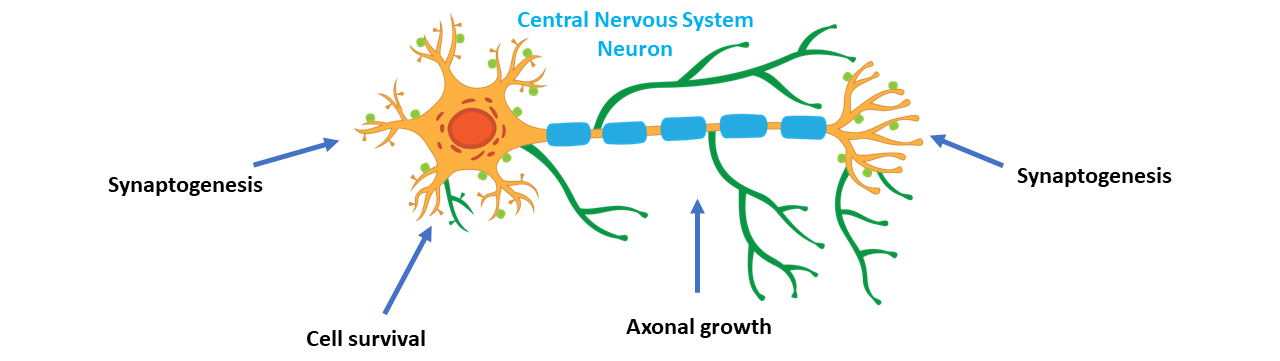
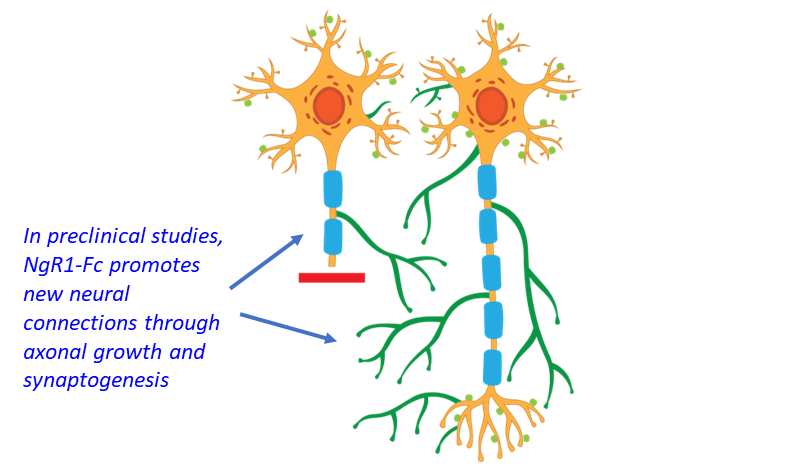
ReNetX is developing Nogo Receptor decoy as an orthogonal approach to maintaining and recovering visual function independent of stress (i.e., pressure, abnormal vascularization, inflammation, etc.). In the context of glaucoma, Nogo Receptor decoy is being developed to treat patients that continue to experience loss of vision despite treatment with current standard of care for lowering ocular pressure. The target profile is to stop or reduce the decline in visual function with neuroenhancement upon initiation of treatment due to repair of damaged synaptic connections.